Camel spiders have captured the public’s imagination with tales of their monstrous size and terrifying behavior. Often painted as bloodthirsty creatures, these arachnids are the subject of widespread rumors and myths. But how much of what you’ve heard about camel spider is true?
In this article, we will separate fact from fiction and explore what these creatures are really like. Whether you’re curious about their size, speed, or feeding habits, keep reading to uncover the truth.
What Are Camel Spiders?

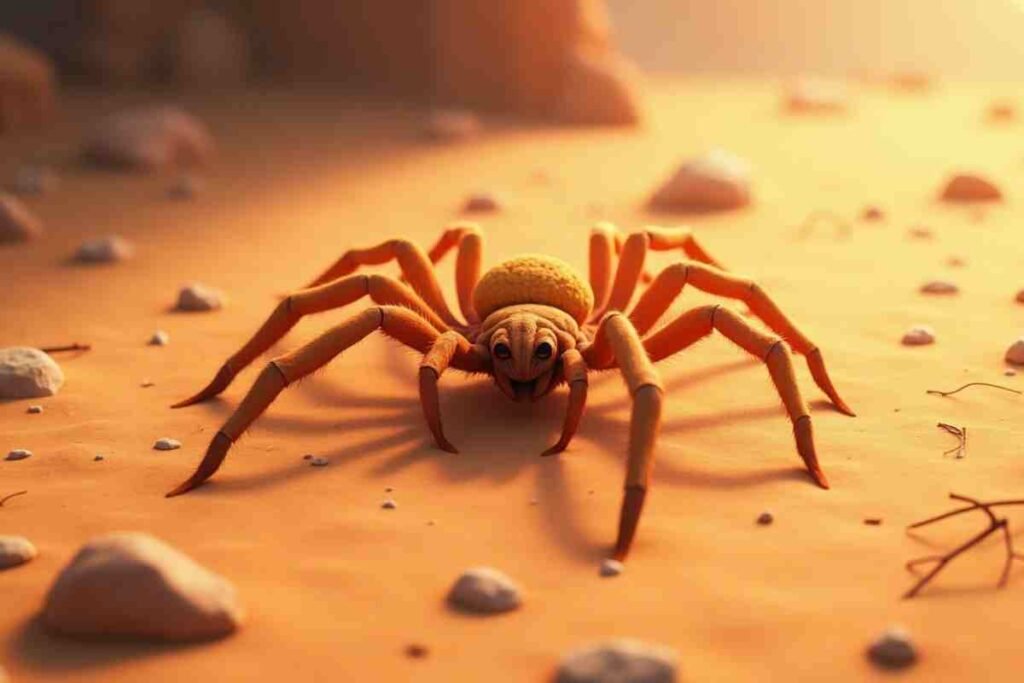
Camel spiders, scientifically known as Galeodes arabs, are not actually spiders at all. They belong to the solpugid family, a group of arachnids that are distinct from true spiders.
Though commonly referred to as “camel spider,” these creatures are more accurately described as wind scorpions or sun spiders.
They are known for their large size and impressive speed, but much of what is commonly believed about them is based on myths.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Galeodes arabs |
| Common Name | Camel Spider, Wind Scorpion, Sun Spider |
| Family | Solpugidae |
| Size | Typically 6 inches (15 cm) in length |
| Speed | Up to 10 miles per hour (not 25 mph) |
| Diet | Insects, small mammals, lizards, birds |
| Habitat | Deserts, nocturnal, seek shelter during the day |
| Venomous | Not venomous, bites can be painful but not life-threatening |
| Lifespan | Up to one year, depending on environmental conditions |
| Behavior | Solitary hunter, uses strong jaws to capture and consume prey |
Myth #1: Camel Spiders Are Huge and Deadly
One of the most popular myths is that camel spiders are gigantic creatures that can grow as large as a human’s torso. In reality, they typically measure about 6 inches in length.
Some images circulating online, particularly during the Iraq War, have used false perspectives to make camel spider appear much larger than they actually are.
These images exaggerate the creature’s size, often placing them closer to the camera lens to create a sense of scale that is not accurate.
In truth, spiders are not as enormous as they are often depicted. Their actual size is manageable, and they are not the monstrous creatures some believe them to be.
Myth #2: Camel Spiders Can Run at 25 Miles Per Hour
Another common misconception is that camel spiders can run at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour. This claim, widely circulated in online forums and emails, is simply not true.
Camel spiders are fast, especially compared to other arachnids, but their maximum speed is around 10 miles per hour. In some instances, reports have even cited speeds of less than 1 mile per hour when measured accurately.
The reason for the exaggerated speed is partly due to the species’ quick movements when seeking shelter, such as when they scurry toward shade in the desert. These fast bursts of movement have contributed to the myth of their high-speed abilities.
Myth #3: Camel Spiders Lay Eggs Under Camels’ Skin

Perhaps one of the most bizarre myths is that camel spiders lay their eggs under camels’ skin. This tale likely started from the observation that camel spider are often seen around camels in the desert. However, this is purely coincidental. Camel spider do not lay eggs in camels or any other mammals.
Instead, camel lay their eggs in the soil, where the larvae hatch and begin their predatory life cycle. Their diet mainly consists of insects, small mammals, lizards, and birds, not the stomachs of camels.
Myth #4: Camel Spiders Are Venomous
Another myth is that camel spiders are venomous and can bite through flesh, leaving holes or even causing death. While camel spiders do possess strong jaws, they are not venomous. They do not have the ability to inject venom into their prey.
Instead, camel use their powerful jaws to capture and crush their prey. They then release digestive fluids to liquefy the flesh, which allows them to consume it efficiently.
Although their bites can be painful, they are not life-threatening. In rare cases, a bite may lead to infection, but this is more likely due to improper care of the wound rather than the spider’s toxicity.
Why Camel Spiders Are Misunderstood
The myths surrounding camel spiders often stem from misidentifications, cultural stories, and exaggerated accounts shared via the internet. For example, during the Iraq War in 2003, stories about camel spider’s grew in popularity, with many soldiers spreading rumors about their terrifying size and behavior.
Some stories claimed that camel spiders could jump as high as 4-6 feet or even chase people down, but these stories are simply fabricated.
Camel Spiders in Their Natural Habitat

Camel spiders thrive in desert climates, where they hunt at night and seek shelter during the day. Their natural prey includes insects, small rodents, and reptiles, which they hunt with remarkable skill.
Their large, powerful jaws are designed to grab and tear into their prey, while their agile legs help them move quickly across the desert sands in search of food.
These arachnids have adapted to survive in some of the harshest environments on Earth.
Their behavior is not one of bloodthirstiness, but rather survival. Spiders are solitary hunters that depend on their instincts and predatory skills to stay alive in the unforgiving desert.
Conclusion
While camel spiders have been the subject of many myths and exaggerations, the truth is far less terrifying. These creatures, though large and fast for an arachnid, are not the deadly monsters some people believe them to be.
They are important predators in their ecosystem and play a vital role in controlling the populations of smaller animals.
By understanding the real facts about camel spider, we can separate myth from reality and gain a deeper appreciation for these fascinating creatures. The next time you hear a wild story about camel spiders, you’ll know the truth.
FAQs
Are Spiders dangerous to humans?
No, camel spiders are not dangerous to humans. While their bite can be painful, they are not venomous and pose no significant health threat.
How fast can camel spider’s run?
Camel spider’s can run up to 10 miles per hour, but the 25 miles per hour claim is a myth.
Do spiders live in other parts of the world?
Yes, Spiders are found in deserts worldwide, including the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of North America.
Can spiders jump?
Spiders can move quickly and have strong legs, but they cannot jump 4-6 feet as some myths suggest.
Why do camel spiders seek shade?
Camel spiders are nocturnal creatures and seek shade during the hot day to protect themselves from the harsh desert sun.
How long do spiders live?
In the wild, Spiders typically live up to one year, though their lifespan can vary depending on environmental conditions.
Do spiders eat camels?
No, it do not eat camels. They primarily hunt smaller prey like insects, lizards, and rodents.
Are camel spider solitary or social?
Camel spider are solitary hunters. They do not live in colonies and typically hunt alone.